What Is EMKG and Why Is It So Important for Workplace Safety?

Managing the risks of workplace chemicals without a clear system is a recipe for disaster. It's like navigating a maze blindfolded—you’re bound to hit a wall. This is where the EMKG method comes in, offering a systematic and practical roadmap for chemical safety.
Developed by Germany's Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (BAuA), EMKG stands for "Einfaches Maßnahmenkonzept Gefahrstoffe," which translates to "Easy-to-use Workplace Control Scheme for Hazardous Substances." It is a structured framework designed to help employers conduct a systematic risk assessment and manage the dangers associated with using chemicals at work.
Instead of getting bogged down in costly and complex air monitoring, EMKG provides a straightforward, qualitative approach. It acts like a traffic light for chemical risk, helping you quickly classify workplace situations as low-risk (green), requiring more attention (yellow), or needing immediate and robust controls (red). This simplicity makes it a game-changer, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may not have a team of industrial hygienists on standby.
More Than Just a Compliance Checklist
At its core, the EMKG framework is designed to make the daunting task of chemical risk assessment manageable. It breaks the entire process into logical, bite-sized steps, giving companies a reliable way to protect their employees without needing a Ph.D. in toxicology.
By focusing on real-world factors, it shifts the perspective on compliance. Instead of being a reactive chore, safety becomes a proactive tool for building a better, safer workplace.
The entire methodology is built on a few core principles of systematic risk assessment:
- Identify the Hazard: First, you must understand the inherent dangers of the substance. EMKG begins by identifying these dangers using information pulled directly from the Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
- Assess the Exposure: Next, it examines how people actually come into contact with the chemical. This includes how much they use, how long they are exposed, and the physical process (e.g., spraying vs. wiping).
- Implement Controls: Finally, it combines the hazard and exposure information to group risks into "control bands." Each band points to a specific set of pre-defined protective measures.
This structured process does more than just help you meet regulations like OSHA in the U.S. or REACH in Europe. It builds a genuine safety culture by making risk management understandable for everyone, not just safety professionals. For a look at modern digital tools that simplify this, you can explore chemical risk assessment solutions.
The EMKG method isn't just about ticking boxes for an auditor. It's about creating a living, breathing safety system. It provides a shared language for discussing chemical risks, ensuring everyone from procurement to the shop floor understands their role in maintaining a safe workplace.
By cutting through the complexity, EMKG empowers teams with the clarity and confidence needed to handle the challenges of chemical management head-on.
The Four Pillars of the EMKG Framework
At its core, the EMKG process is a logical, four-step journey. Think of it like a detective solving a case: you gather clues (information), determine how dangerous the situation is (hazard), identify who’s at risk (exposure), and finally, decide on the best way to protect everyone (controls).
Each step in this systematic risk assessment framework builds on the previous one, creating a comprehensive and reliable picture of the chemical risks your team faces. It replaces guesswork with a clear, straightforward method for turning data into action.
Let's walk through each of these pillars one by one.
Pillar 1: Gathering Information
Every good risk assessment starts with good information. This first step is all about collecting the essential facts about the substances you're working with. After all, you can't protect your team from a hazard you don't fully understand.
Your single most important tool here is the Safety Data Sheet (SDS). This document is a treasure trove of information provided by the manufacturer. For the EMKG method, you'll need to focus on a few key details:
- Hazard Statements (H-Statements): Standardized phrases that describe specific dangers, like "H319: Causes serious eye irritation."
- Physical State: Is the chemical a solid, a liquid, or a gas?
- Volatility/Dustiness: How easily does it become airborne and inhalable?
Getting this first step right is non-negotiable. If your initial information is flawed, the entire assessment will be unreliable. Solid data is the foundation for everything that follows.
Pillar 2: Assessing Hazard Potential
Once you have the facts, it's time to interpret them. The second pillar, Assessing Hazard Potential, involves translating the technical data from the SDS into a simple hazard category. This step is purely about the substance's inherent properties—its capacity to cause harm upon contact.
The EMKG model simplifies this by grouping chemicals based on their H-statements. For instance, a chemical that is highly toxic if inhaled will fall into a much higher hazard group than one that is only a mild skin irritant. At this stage, you’re not considering how the chemical is used, only its intrinsic danger.
It’s like knowing the difference between a house cat and a lion. Both are felines, but their inherent potential to cause harm is vastly different. This pillar ensures you understand exactly what you're dealing with from the start.
Pillar 3: Assessing Exposure
A hazardous chemical sitting untouched on a shelf poses little threat. The risk only becomes real when people are exposed to it. That's what the third pillar, Assessing Exposure, is all about—evaluating how employees interact with the substance in their actual work environment.
Here, you'll examine the practical details of the task:
- Quantity Used: Are people handling a few milliliters or a 55-gallon drum?
- Method of Application: Is the chemical being brushed on, sprayed as an aerosol, or used in an open dipping tank?
- Duration and Frequency: How long does the task last, and how often is it performed?
This is where context becomes king. A highly hazardous substance in a completely sealed, automated system might pose a lower risk than a less hazardous one being splashed around all day in a poorly ventilated room. Assessing exposure turns a theoretical danger into a real-world risk level.
Pillar 4: Selecting Controls
The final pillar, Selecting Controls, is where the systematic assessment culminates in action. By combining the hazard potential from Pillar 2 with the real-world exposure from Pillar 3, the EMKG matrix directs you to a set of recommended safety measures.
This is the ultimate payoff of the process. Instead of guessing or applying a one-size-fits-all safety rule, you select controls that are perfectly matched to the specific risk you've identified.
These measures follow the hierarchy of controls, ranging from simple ventilation upgrades and basic PPE to a complete re-engineering of the process itself. It ensures your safety efforts are targeted, effective, and resource-efficient.
How to Perform an EMKG Risk Assessment Step by Step
Understanding the theory is one thing, but putting EMKG into practice is where its value truly shines. Let's walk through a complete, systematic risk assessment for a common scenario: handling an industrial cleaning solvent.
The goal of the EMKG process is to provide a logical path from complex chemical data to clear, actionable safety steps. This visual flowchart breaks down the four core pillars, showing how you move from gathering information all the way to implementing controls.
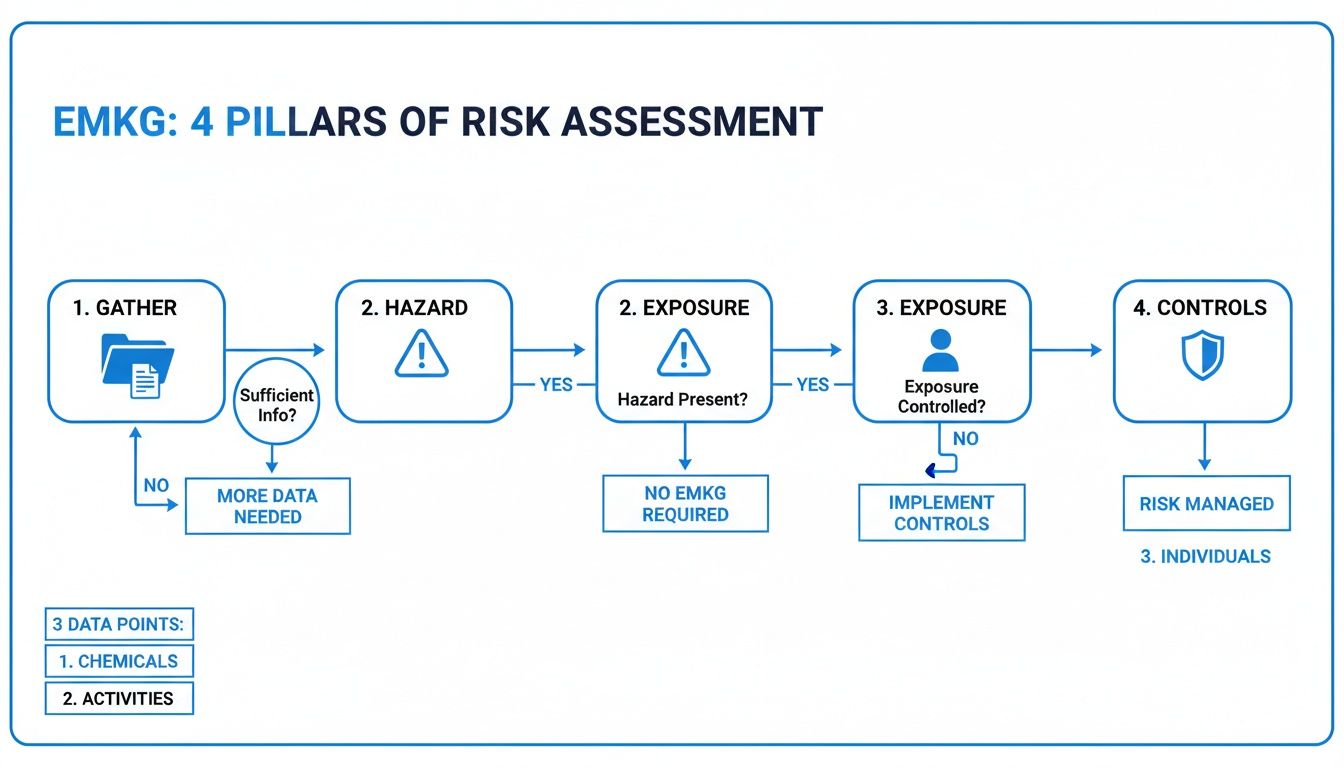
As the chart shows, the process flows naturally: you gather your data, identify the hazards, assess the real-world exposure, and finally, select the right controls. It’s a systematic and repeatable workflow built for any workplace that handles chemicals.
Step 1: Gather Information from the Safety Data Sheet
First things first: you need accurate information. Your single most important document for any chemical is its Safety Data Sheet (SDS). The SDS is the bedrock of the entire assessment, packed with standardized information straight from the manufacturer.
For our industrial cleaning solvent, you’d grab its SDS and go straight to Section 2, "Hazards Identification." This is where you’ll find the critical pieces for your EMKG analysis:
- GHS Pictograms: Diamond-shaped symbols with red borders that give a quick visual warning (e.g., flame, skull and crossbones, health hazard).
- Signal Word: Either "Danger" or "Warning," indicating the relative severity of the hazard.
- Hazard Statements (H-Statements): Standardized phrases that specify the danger, like "H315: Causes skin irritation" or "H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness."
This initial data collection is non-negotiable. Without a current and complete SDS, you cannot perform an accurate risk assessment. The growing global market for SDS management, projected to hit $25.4 billion by 2033 from $1.2 billion in 2023, underscores how seriously organizations are taking this foundational step.
Step 2: Determine the Hazard Group
With the H-statements in hand, your next task is to map this information to the correct EMKG hazard group. The EMKG system simplifies toxicology by categorizing substances into groups based on their potential to cause harm via different exposure routes (inhalation, skin contact, etc.).
Let's imagine our solvent's SDS lists:
- H-Statements: H226 (Flammable liquid and vapor), H319 (Causes serious eye irritation), H336 (May cause drowsiness or dizziness).
- Pictograms: Flame, Exclamation Mark.
To translate this information, you use a table that maps GHS data from the SDS to EMKG hazard groups.
EMKG Hazard Groups and Corresponding GHS Indicators
| EMKG Hazard Group | Description | Common GHS H-Statements | Relevant GHS Pictogram(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | High Hazard (Inhalation): Materials that can cause serious or irreversible health effects from breathing them in. | H330, H331, H334, H340, H350, H360 | Skull and Crossbones, Health Hazard |
| B | Medium Hazard (Inhalation): Materials that can cause moderate health effects from breathing them in. | H332, H335, H371, H373 | Exclamation Mark, Health Hazard |
| C | Low Hazard (Inhalation): Materials causing minor, reversible effects like dizziness or irritation from inhalation. | H336 | Exclamation Mark |
| D | Skin/Eye Contact Hazard: Materials that are corrosive or irritating to the skin or eyes. | H314, H315, H317, H318, H319 | Corrosion, Exclamation Mark |
| E | Fire/Explosion Hazard: Materials that are flammable, self-heating, or could explode. | H220-H228 | Flame, Flame over circle, Exploding bomb |
Using this table, we can see our solvent's H336 statement places it in Hazard Group C for inhalation, while H319 places it in Hazard Group D for skin/eye contact. You've just translated complex chemical language into simple, usable risk categories.
Step 3: Assess the Exposure Potential
Now we pivot from the chemical's inherent dangers to how your team actually uses it. This step is all about understanding the reality of the task and the workplace environment.
You need to ask practical questions:
- Quantity Used: Is the employee using a small spray bottle (low quantity) or pouring from a 55-gallon drum (high quantity)?
- Release Potential: Is the solvent carefully wiped onto a surface (low volatility/release) or sprayed as an aerosol that hangs in the air (high dispersion)?
- Work Environment: Is the job performed in a large, well-ventilated workshop or a small, enclosed room with poor airflow?
For our scenario, let's say a worker uses a spray bottle (small quantity) to apply the solvent onto machine parts in a large, open workshop with good general ventilation. In the EMKG framework, this combination of factors would most likely result in a low exposure level.
Step 4: Combine and Find Your Control Strategy
This final step is where the systematic risk assessment comes together. You use the EMKG matrix, a simple grid that plots your hazard group (from Step 2) against the exposure level (from Step 3).
The beauty of the EMKG matrix is its simplicity. It cross-references the "how dangerous is it?" question with the "how are we using it?" question to deliver a specific, actionable answer.
In our example, a low-to-moderate hazard (Groups C and D) combined with a low exposure level would point to a specific control band, likely "Control Strategy 100." This code corresponds directly to a pre-written Control Guidance Sheet (CGS).
That CGS provides clear, practical instructions—no jargon, just actions. It would likely recommend ensuring good general ventilation and using standard personal protective equipment (PPE) like safety glasses and gloves. And with that, you've completed the cycle—from complex SDS data to concrete, targeted safety measures that address the real-world risk. For more insights on this topic, check out our guide on improving chemical safety in the workplace.
Weaving EMKG into Your Broader Safety Program
A single risk assessment is a snapshot in time, but a true safety culture is a living process. To genuinely protect your team, the EMKG methodology can't be a one-off task. It must be woven into the fabric of your organization’s safety management system, acting as a dynamic engine that drives continuous improvement.
When you elevate EMKG from a simple compliance tool to a core strategic element, you build a proactive and resilient chemical safety culture. This integration ensures safety is a key consideration at every stage of a chemical's lifecycle in your workplace, from procurement to disposal.
The process starts long before a new substance ever hits your loading dock.
Start with Smarter, Proactive Procurement
One of the most powerful applications of the EMKG framework is during procurement. Instead of reacting to the risks of chemicals you already have, you can use EMKG to screen potential new products before they're purchased. This simple shift moves your safety posture from reactive to proactive.
Imagine a department requests a new cleaning agent. The procurement and Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) teams can perform a quick, preliminary EMKG assessment:
- Request the SDS: Ask the potential supplier for the Safety Data Sheet for the new chemical.
- Run a Preliminary Assessment: Use the SDS to determine the chemical’s hazard group and estimate the likely exposure based on its intended use.
- Compare Options: Evaluate several products for the same job, using their EMKG risk profiles as a key decision-making factor.
This proactive screening helps you choose safer alternatives from the start, effectively engineering risk out of your processes. It’s a foundational piece of any truly robust safety program.
Create Training That Actually Sticks
Generic safety training often fails to resonate with employees. People need to understand the specific risks they face daily, not just abstract rules. The findings from your EMKG assessments provide the perfect blueprint for creating relevant and effective training programs.
Instead of another generic "Hazard Communication" slideshow, you can build training modules specific to a role. For example, a session for your maintenance crew could focus directly on the solvents and lubricants they use, clearly explaining the specific EMKG control measures identified for those tasks.
When you base training on EMKG results, you connect the dots for your team. They see precisely how the rules—like wearing certain gloves or using local exhaust ventilation—are directly tied to the real-world hazards of the chemicals they handle.
This targeted approach makes information more engaging and memorable, increasing the likelihood that safety protocols will be followed correctly. To ensure these guidelines are always accessible, a central company knowledge base can be an invaluable resource.
Sharpen Your Emergency Preparedness
A thorough EMKG assessment does more than guide day-to-day safety; it also significantly strengthens your emergency preparedness. By systematically identifying worst-case scenarios for each hazardous substance, you can create targeted and practical emergency response plans.
The EMKG process helps pinpoint which chemicals pose the greatest fire, inhalation, or corrosive risks. This information is critical for:
- Spill Response: Developing specific cleanup procedures based on a chemical’s unique properties.
- First Aid: Equipping first aid stations with the right supplies and training first responders on specific symptoms of exposure.
- Evacuation Planning: Identifying high-hazard areas that require prioritization during an evacuation.
Unfortunately, many organizations still manage this vital safety data with outdated tools like spreadsheets, which often lead to version control issues and compliance gaps. Transitioning to a modern, automated solution is a major step toward enhancing chemical safety.
Ultimately, integrating EMKG turns it from a procedural chore into a strategic asset. It provides the data-driven foundation for smarter purchasing, more effective training, and confident emergency preparedness. You can explore various risk and safety solutions for your organization to see how this fits into a bigger picture.
How Technology Can Make Your EMKG Process Easier

While the EMKG method provides a clear, logical path for systematic risk assessment, performing it manually can be slow, tedious, and prone to human error. Sifting through hundreds of Safety Data Sheets to extract H-statements and document every scenario is a significant administrative burden.
This is where modern technology changes the game.
Tools like the NextSDS platform are designed to automate these repetitive, time-consuming steps, transforming a complex manual chore into a consistent, efficient digital process. This frees up your Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) team to focus on higher-value activities, like implementing safety controls and fostering a proactive safety culture.
Instead of drowning in paperwork, imagine a system that does the heavy lifting, providing instant clarity and a perfect audit trail.
Automating Data Extraction and Hazard Grouping
The entire EMKG assessment hinges on accurate data from the SDS. Manually transcribing hazard statements, CAS numbers, and physical properties is not just tedious—it’s a recipe for typos that can invalidate the entire assessment. Automation eliminates this risk.
Modern chemical management platforms use smart data extraction to pull critical information directly from your SDS library:
- Intelligent Parsing: The system "reads" each SDS, identifying and capturing key data points like H-statements, pictograms, and signal words.
- Instant Mapping: It then automatically and accurately maps this data to the correct EMKG hazard groups (A, B, C, D, E).
- Error Elimination: By removing manual data entry, the risk of human error is virtually eliminated. Your hazard identification is correct, every single time.
This automated first step creates a rock-solid foundation, ensuring the rest of your EMKG risk assessment is built on trustworthy information.
Simplifying Exposure Assessment and Control Selection
Once the hazard is identified, the next step is to assess exposure. Technology helps standardize this process by guiding users through a structured evaluation of their workplace conditions. A digital platform can use simple forms and dropdown menus to capture key variables consistently.
Think of a digital EMKG tool as a co-pilot for your safety team. It doesn't just store data; it actively guides the assessment, ensuring consistency and preventing critical oversights.
The system then combines the automatically-grouped hazard information with the user-entered exposure details. Using the built-in EMKG matrix logic, it instantly calculates the risk level and points directly to the appropriate Control Guidance Sheet. This creates a seamless, connected workflow—from SDS to specific control measures—all within a single platform.
Creating a Single Source of Truth for Compliance
Perhaps the greatest benefit of using technology for EMKG is the creation of a central, auditable record of all risk assessments. Every decision, assessment, and control measure is documented in one place, establishing a powerful single source of truth for your entire chemical inventory.
This delivers several major advantages:
- Consistency: Every assessment follows the same digital workflow, ensuring a standard approach across all sites and departments.
- Auditability: When an auditor requests documentation, you can generate a comprehensive report in seconds, demonstrating a robust and systematic risk management process.
- Accessibility: Risk assessments are no longer buried in filing cabinets. The entire safety team can access them, fostering better collaboration and oversight.
For any organization facing a mountain of paperwork, it's worth exploring how tools like document processing automation can streamline data handling. By digitizing the EMKG methodology, you can move beyond mere compliance and build a smarter, more responsive chemical safety program.
Got Questions About EMKG? We've Got Answers.
Adopting a new safety process like EMKG always raises questions. It's one thing to understand the theory, but another to apply it effectively in your workplace. Let's address some of the most common questions that arise when teams begin implementing this systematic risk assessment method.
Think of this as the practical FAQ you need to bridge the gap between the manual and your day-to-day reality.
Is EMKG a Legal Requirement?
This is a key question. The EMKG method originated in Germany and was designed to align with European Union regulations. While it is a recognized standard there, it is not an explicit legal mandate in countries like the United States.
However, regulatory bodies like OSHA have a "general duty clause" that requires employers to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards. EMKG offers a robust, systematic, and well-documented method for fulfilling this obligation. It is considered a best practice for demonstrating due diligence in chemical risk management, even if the law doesn't specify the method by name.
Does EMKG Work for Every Single Chemical?
Almost. The EMKG system is a fantastic tool for the vast majority of chemicals found in a typical workplace, such as cleaners, solvents, lubricants, and manufacturing additives. It is designed for these common risk assessment scenarios.
However, it has limitations. For certain high-risk or unpredictable situations, a more specialized approach is necessary. EMKG may not be suitable for:
- Complex chemical reactions: Where mixing substances could lead to unexpected and dangerous outcomes.
- High-potency carcinogens: Especially those with no known "safe" exposure level.
- Chemicals with incomplete information: If a complete Safety Data Sheet is unavailable, a proper assessment cannot be performed.
In these cases, a more detailed, quantitative analysis by an occupational hygienist is the appropriate course of action.
How Often Do I Need to Re-Do an EMKG Assessment?
An EMKG assessment is a living document, not a "set it and forget it" task. It must be reviewed and updated whenever there is a significant change in the workplace.
This includes the introduction of a new chemical, a modification to a process or equipment, or the publication of new safety information about a substance. Additionally, if a safety incident occurs, an immediate review is essential.
As a general rule of thumb, even if no changes occur, it is wise to review your assessments every one to two years. This ensures your control measures remain effective and your documentation stays current.
Ready to ditch the confusing spreadsheets and simplify your EMKG process? NextSDS automates the entire chemical risk assessment workflow, from pulling data straight from the SDS to recommending the right controls. See how we make safety and compliance easier at https://nextsds.com.

